New Technologies in Building Construction and Design
The construction and design of buildings are undergoing a significant transformation thanks to advancements in technology. These innovations not only enhance efficiency and sustainability but also improve safety, comfort, and overall functionality. Here, we explore five key technologies that are shaping the future of building construction and management.
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM)

Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a revolutionary technology that allows architects, engineers, and construction professionals to create and manage digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of buildings. BIM goes beyond traditional blueprints by providing a 3D model that incorporates data about materials, costs, schedules, and maintenance.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Collaboration: BIM facilitates better communication among stakeholders, allowing for real-time updates and changes. This collaborative approach minimizes errors and reduces rework.
- Improved Visualization: The 3D models help clients and stakeholders visualize the final product, making it easier to understand design concepts and make informed decisions.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: By simulating the construction process, BIM helps identify potential issues early, reducing delays and costs associated with changes during construction.
Applications: BIM is widely used in large-scale commercial projects, infrastructure development, and residential construction. It enhances project management, streamlines workflows, and improves overall project outcomes.
2. Smart Building Technologies

Smart building technologies integrate various systems within a building to improve efficiency, comfort, and security. These technologies utilize sensors, IoT devices, and automation to monitor and control building operations such as lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC).
Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Smart buildings can significantly reduce energy consumption by optimizing heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy and usage patterns.
- Enhanced Comfort: Automated systems adjust environmental conditions to maintain optimal comfort levels for occupants.
- Improved Security: Smart technologies include surveillance systems, access controls, and alarms that enhance the safety and security of the building.
Applications: Smart building technologies are prevalent in commercial real estate, educational institutions, and healthcare facilities. They contribute to creating more sustainable and user-friendly environments.
3. Prefabrication and Modular Construction
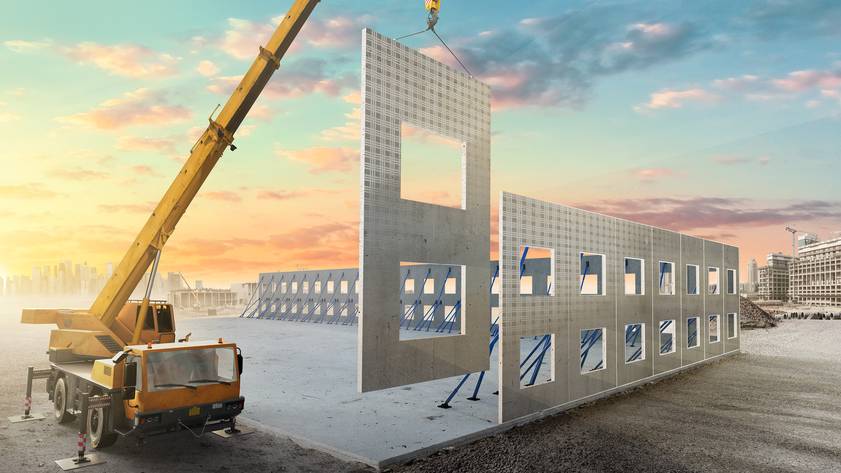

Prefabrication and modular construction involve manufacturing building components off-site in a controlled environment before transporting them to the construction site for assembly. This approach allows for faster construction times and reduced waste.
Advantages:
- Speed of Construction: Prefabricated components can be assembled quickly on-site, significantly reducing construction timelines.
- Quality Control: Manufacturing in a controlled environment ensures higher quality and consistency in building materials and components.
- Reduced Waste: Off-site construction minimizes material waste and allows for better recycling and reuse of materials.
Applications: Prefabrication and modular construction are commonly used in residential housing, commercial buildings, and temporary structures like disaster relief shelters. They are ideal for projects requiring rapid deployment and cost efficiency.
4. Sustainable Building Materials

The use of sustainable building materials is gaining traction as the construction industry seeks to reduce its environmental impact. These materials are sourced responsibly, have a lower carbon footprint, and contribute to energy efficiency.
Advantages:
- Environmental Benefits: Sustainable materials help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote resource conservation.
- Healthier Indoor Environments: Many sustainable materials are non-toxic and contribute to better indoor air quality, enhancing occupant health and comfort.
- Long-term Cost Savings: While initial costs may be higher, sustainable materials often lead to lower energy bills and maintenance costs over time.
Applications: Sustainable building materials are used in various projects, including residential homes, commercial buildings, and public infrastructure. Examples include recycled steel, bamboo, reclaimed wood, and low-VOC paints.
5. Energy Management Systems (EMS)
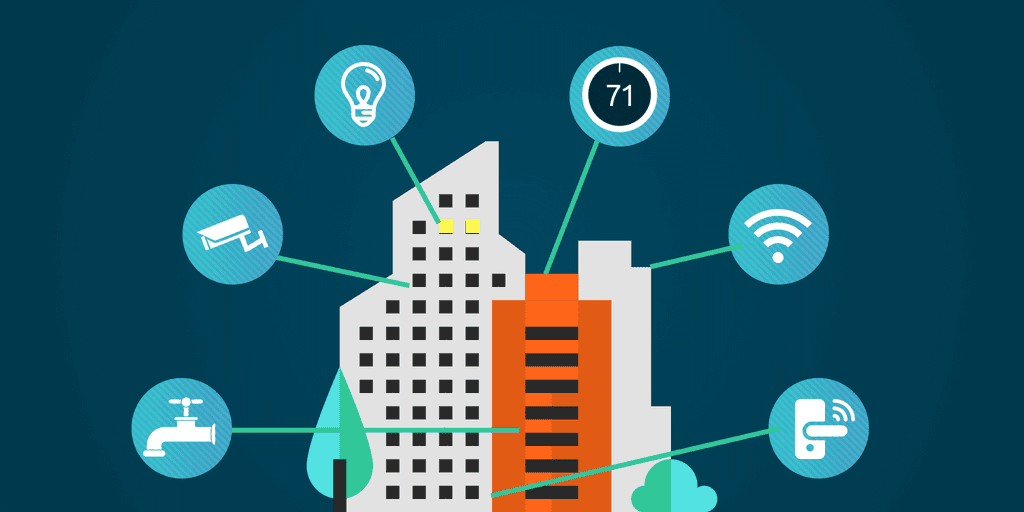
Energy Management Systems (EMS) are integrated platforms that monitor, control, and optimize energy usage within a building. These systems utilize data analytics and real-time monitoring to improve energy efficiency and reduce costs.
Advantages:
- Real-time Monitoring: EMS provides insights into energy consumption patterns, helping building managers identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Cost Reduction: By optimizing energy usage, EMS can significantly lower utility bills and operational costs.
- Sustainability Goals: EMS supports organizations in achieving their sustainability targets by reducing overall energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Applications: Energy Management Systems are widely used in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and educational institutions. They play a crucial role in managing energy resources effectively and promoting sustainable practices.
Conclusion
The integration of new technologies in building construction and management is transforming the industry, making it more efficient, sustainable, and user-friendly. From Building Information Modeling (BIM) to smart building technologies, prefabrication, sustainable materials, and energy management systems, these innovations are reshaping how we design, construct, and operate buildings.
As the demand for sustainable and efficient buildings continues to grow, embracing these technologies will be essential for architects, builders, and property managers. By leveraging these advancements, the construction industry can meet the challenges of the modern world while creating spaces that are not only functional but also environmentally responsible and comfortable for occupants.




No comment